Is COVID-19 An Occupational Disease under New Hampshire Worker’s Compensation Law?
As addressed in previous articles, there will be worker's compensation coverage available for many employees who contract COVID-19 at work. The most likely path to this coverage will be with the understanding that the employee became ill due to a neutral risk, but that the employee faced a greater risk of getting ill due to his or her work, as compared to the general public. This is known as the increased risk test and employees who can show this will likely find coverage available for lost wages, medical bills and job protections.
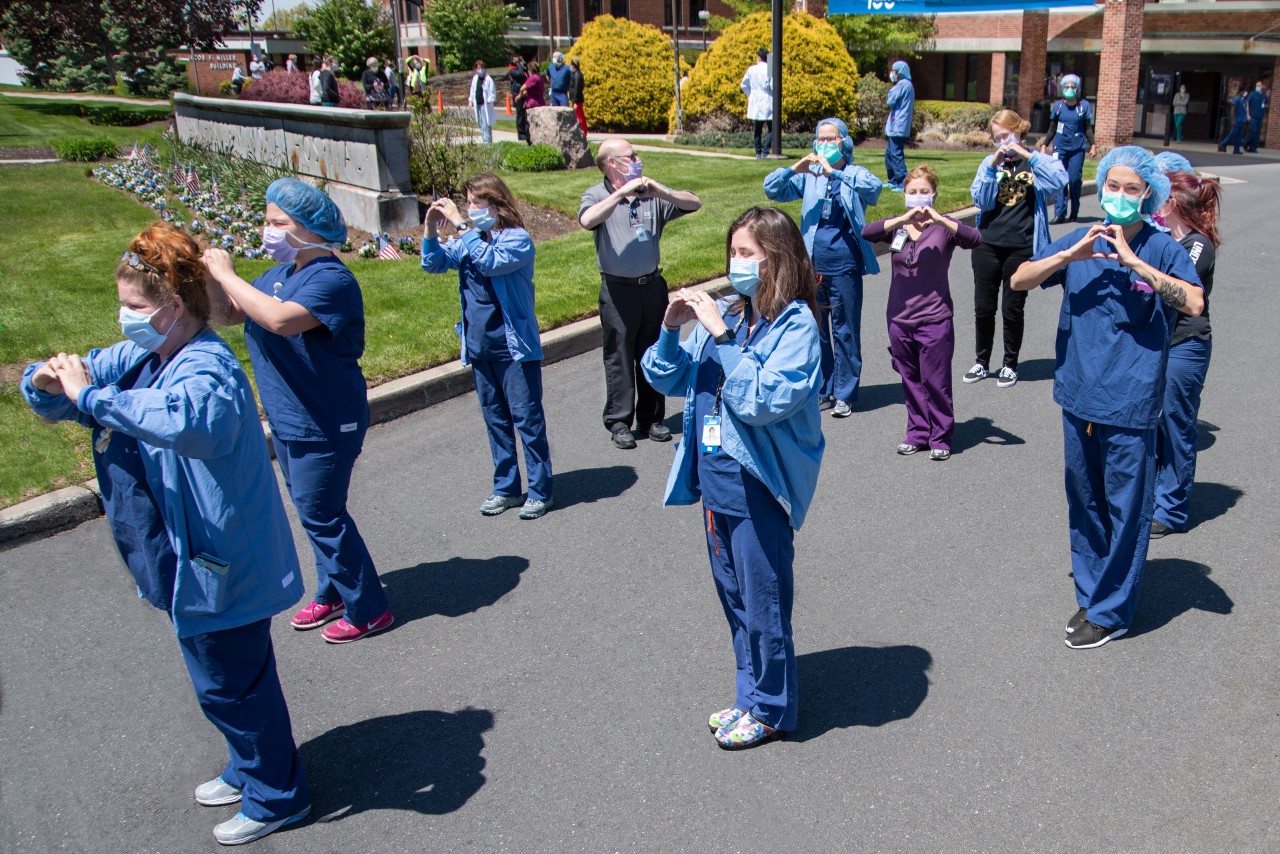
However, healthcare workers who treat patients with diagnoses of COVID-19 may have more than one route to winning coverage should they contract COVID-19. Certainly, these workers should be able to show they are at increased risk of contracting the illness as compared to members of the general public due to the work they do and to the correlating increased frequency of direct exposure to illness, even if no specific transmission of the disease can be traced to a known carrier. If the healthcare worker has had to engage in care that entails unusually contagious situations, such as exposures in the process of resuscitation or intubation or without full PPE, the fact that their risk was increased due to the qualitative nature of their work is clear.
That said, there may be an argument to be made that these workers or those in similar circumstances, may alternatively be eligible for workers’ compensation benefits under NH RSA 281-A:2 XIII: Occupational Disease.
RSA 281-A:2 XIII Occupational Disease
In accordance with RSA 281-A:2 XIII “Occupational disease” is “...an injury arising out of and in the course of the employee’s employment and due to causes and conditions characteristic of and peculiar to the particular trade, occupation or employment. It shall not include other diseases or death therefrom unless they are the direct result of an accidental injury arising out of or in the course of employment...”